Blood sample collection tubes, used in clinical laboratories and hospitals, are among the important tools for starting any analysis or examination.
The Vacuum Tube system (Vacutainer) for collecting blood used in various laboratory tests consists of tubes of various sizes, with colored caps indicating the contents of the tube. Most blood-collecting tubes contain an additive that either speeds up blood clotting (clot promoter) or prevents blood clotting (anticoagulant).
and for the different types of laboratory tubes, their uses, and even their sizes, they have been defined globally by reference to distinctive colors that distinguish them from each other, What is the color, what are the primary colors, and what do they indicate?

What are the Colors of the Blood Sample Collection Tubes and their Uses?
Blood Sample Collection Tubes with Purple Cap
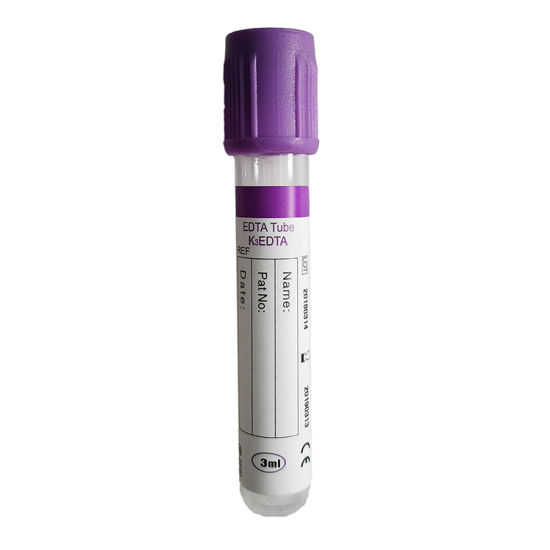

The Purple blood sample collection tubes contain an anticoagulant called EDTA, which is a short name for ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid, as this substance binds to calcium in the blood, preventing it from clotting.
These tubes are also used in comprehensive blood tests, which require the whole blood sample and all of its cells. Examples of tests that require this type are:
- Blood complete CBC test.
- ESR erythrocyte sedimentation rate.
- HbA1C cumulative blood sugar test.
Dealing with this type of test tube requires making sure that the blood is mixed with the anticoagulant, so it must be stirred for 8 minutes to mix well, by turning it frequently.
Blood Sample Collection Tubes with Pink Cap
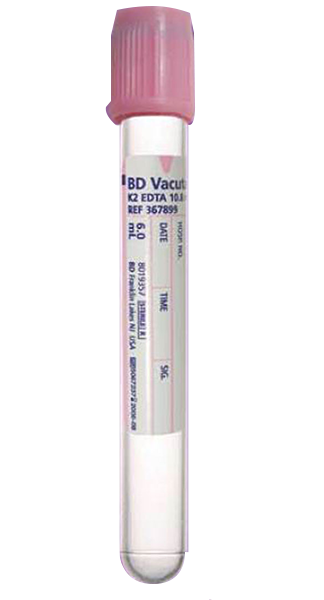
It works with the same purple tube mechanism, but it is used more in blood transfusion analyses of blood samples, as it also contains the anticoagulant substance EDTA, and is used to examine the patient’s blood group, then compare it with other types to reach the appropriate type for the blood transfusion, or the so-called cross match, As for the method of its use, it is similar to the first type in that, as you need constant stirring to mix with the substance, an anti-coagulant.
Blood Sample Collection Tubes with Blue Cap
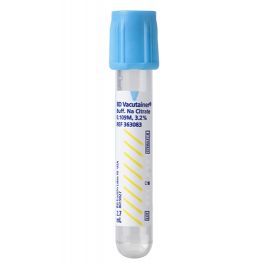
Generally used for haematology tests, contains sodium citrate; As a reflective agent for blood clotting, Sodium citrate binds to calcium ions to prevent coagulation so that it is used in blood clotting tests, calculating bleeding time, in addition to important blood coagulation tests such as D-dimer. that the tube shall be filled to the limit, or the line drawn on it; As more, or less than that will not be good for examination.
Blood Sample Collection Tubes with Yellow Cap
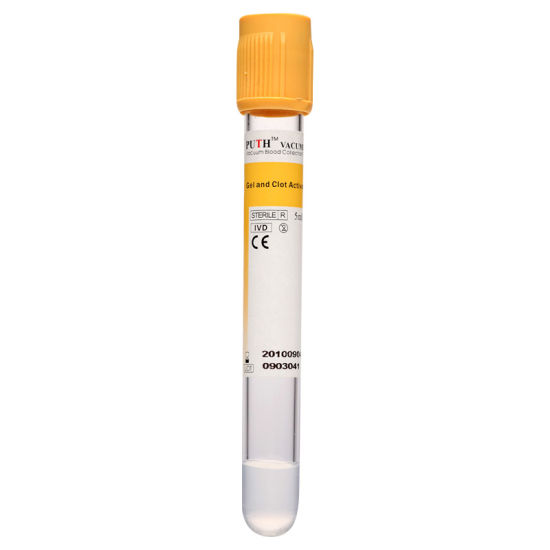
This type of test tube is used in most analyses and laboratory tests such as; Blood chemistry, hormones, and other tests, whereby it is based on the separation of blood serum, through silica particles, and gel, so that the silica particles accelerate blood clotting and coagulation, while the gel separates red blood cells from plasma by floating Between them, then using a centrifuge, the blood serum is separated and will be in the upper yellow layer.
Examples of the tests that can use this tube are the following:
- Biochemistry analyses such as; Fats, kidney and liver function tests, thyroid tests, and vitamins such as vitamin B12.
- Endocrine examinations such as; Cortisol, and sex hormones.
- Analyses of tumor markers.
- Blood toxicology tests.
- Microbiology and immunology tests.
Read Also
- Transforming Patient Care with Professional Healthcare Transcription Services
 In today’s fast-paced healthcare environment, the need for precise and timely documentation cannot be overstated. Accurate documentation is not merely an ancillary task; it is a core element of delivering high-quality patient care. The ability to maintain compliance with regulations, enhance operational efficiency, and ensure… Read more: Transforming Patient Care with Professional Healthcare Transcription Services
In today’s fast-paced healthcare environment, the need for precise and timely documentation cannot be overstated. Accurate documentation is not merely an ancillary task; it is a core element of delivering high-quality patient care. The ability to maintain compliance with regulations, enhance operational efficiency, and ensure… Read more: Transforming Patient Care with Professional Healthcare Transcription Services - Essential Steps to Launch Your Own Optometry Practice
 Launching your own optometry practice can be a thrilling and fulfilling journey. However, it requires careful planning, dedication, and an understanding of what it takes to succeed. With the growth in demand for eye care, more and more individuals are seeking to start their own… Read more: Essential Steps to Launch Your Own Optometry Practice
Launching your own optometry practice can be a thrilling and fulfilling journey. However, it requires careful planning, dedication, and an understanding of what it takes to succeed. With the growth in demand for eye care, more and more individuals are seeking to start their own… Read more: Essential Steps to Launch Your Own Optometry Practice - Compounding Pharmacy: Personalized Medication Solutions
 A compounding pharmacy plays a vital role in modern healthcare by providing customized medications tailored to the specific needs of individual patients. Unlike mass-produced drugs manufactured by pharmaceutical companies, compounded medications are prepared by licensed pharmacists who carefully combine, adjust, or modify ingredients to create… Read more: Compounding Pharmacy: Personalized Medication Solutions
A compounding pharmacy plays a vital role in modern healthcare by providing customized medications tailored to the specific needs of individual patients. Unlike mass-produced drugs manufactured by pharmaceutical companies, compounded medications are prepared by licensed pharmacists who carefully combine, adjust, or modify ingredients to create… Read more: Compounding Pharmacy: Personalized Medication Solutions - The Best Business Decision a Surgeon Ever Made: Ordering a Medical Equipment Appraisal
 Most surgeons don’t go into medicine because they love spreadsheets, valuations, or negotiating buy-ins. They go into medicine because they want to operate, treat patients, and build something meaningful over time. For one surgeon, that mindset worked perfectly, until the day another surgeon decided to… Read more: The Best Business Decision a Surgeon Ever Made: Ordering a Medical Equipment Appraisal
Most surgeons don’t go into medicine because they love spreadsheets, valuations, or negotiating buy-ins. They go into medicine because they want to operate, treat patients, and build something meaningful over time. For one surgeon, that mindset worked perfectly, until the day another surgeon decided to… Read more: The Best Business Decision a Surgeon Ever Made: Ordering a Medical Equipment Appraisal - Creative Approaches to Alleviating Healthcare Staff Shortages
 Hospitals and clinics are facing staff shortages, which makes it harder to take care of patients well. Finding simple and useful solutions is very important. Easy changes like flexible work hours, good training, and chances to grow can help staff stay happy. Technology, like online… Read more: Creative Approaches to Alleviating Healthcare Staff Shortages
Hospitals and clinics are facing staff shortages, which makes it harder to take care of patients well. Finding simple and useful solutions is very important. Easy changes like flexible work hours, good training, and chances to grow can help staff stay happy. Technology, like online… Read more: Creative Approaches to Alleviating Healthcare Staff Shortages
Blood Sample Collection Tubes with Grey Cap
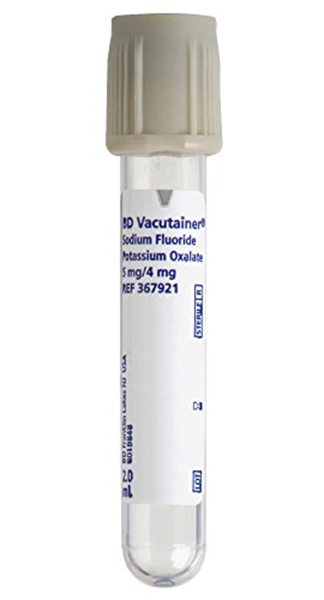
It is rarely used, because it is used for only two tests that can be covered by a yellow capped tube, which are blood glucose (sugar) and lactate test.
This tube contains sodium fluoride; As an antiglycolytic agent to ensure that no further breakdown of glucose occurs within the sample, it also contains potassium oxalate acting as an anticoagulant.
Blood Sample Collection Tubes with Red Cap
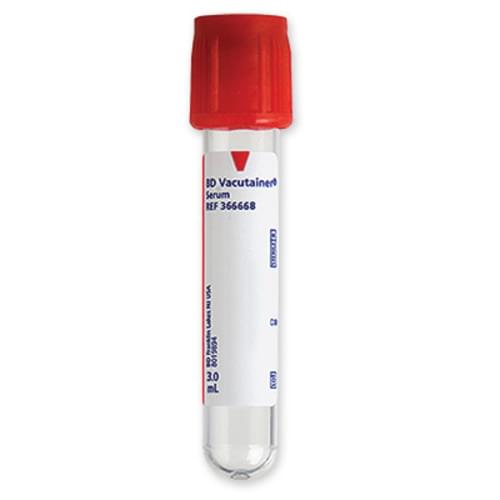
It is not common to use it, it contains silica particles inside it as a clot activator to separate blood serum, it can be used in hormone tests, and toxicology tests, but the yellow color has got all the share in that, and it can be found in the glass form of it.
Blood Sample Collection Tubes with Dark Green Cap

This less frequently used bottle is intended for biochemistry tests that require heparinized plasma, or whole blood for analysis, and can also contain sodium heparin which works as an anticoagulant, common tests performed with a dark green blood sample collection tubes are as follows:
- ammonia
- Insulin.
- Renin, and aldosterone.
Blood Sample Collection Tubes with Light Green Cap
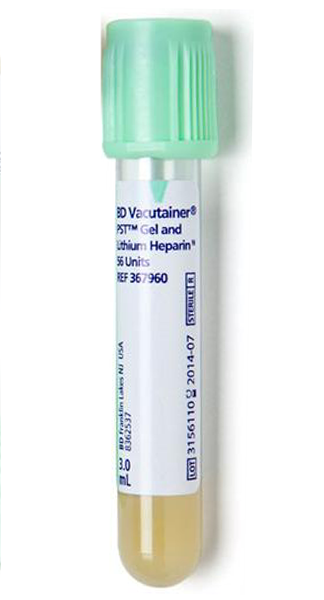
These rare species are used in biochemistry tests that require separated heparinized plasma; It contains lithium heparin, which acts as an anticoagulant, and a plasma separating gel.
Components of Blood
Blood is made up of three main components; These are red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets; Where it can be separated by centrifugation into blood cells and blood plasma, or serum, which contains water, and substances dissolved in it such as antibodies, hormones, and enzymes.
As for the difference between serum and blood plasma, they are similar, but blood plasma contains blood clotting inhibitors found in test tubes, which were mixed with it, while serum does not contain clotting inhibitors, and both are separated by centrifugation, you can also use a mini centrifuge for laboratories.
Types of Blood Samples
Blood samples vary, depending on the location of the withdrawal, and thus can be classified into:
Venous Blood Samples
It is common for blood to be drawn for most samples, and to take a sufficient amount of blood, it is taken from the superficial veins in the elbow of the hand, the wrist, or from the femoral vein.
Arterial Blood Samples
This type of drawing is used to measure blood gases; Such as oxygen and carbon dioxide, and care must be taken when withdrawing from it, and requires good experience in that, it is possible to withdraw from the brachial, or radial, arteries.
Capillary Blood Samples
It is commonly used to know the type or strength of blood so that no large amount of blood is needed. Common sites are the fingertips, the heel, and the earlobe. The heel is commonly used in infants.